R Beginners Course 2025
Introduction to R and Basic Programming Concepts
Bioinformatics Core Facility CECAD
2025-03-17
Slides & Code
- [f] Full screen
- [o] Slide Overview
- [c] Notes
- [h] help
git repo
Clone repo
git clone https://github.com/CECADBioinformaticsCoreFacility/Beginners_R_Course_2025.git
Slides Directly
https://cecadbioinformaticscorefacility.github.io/Beginners_R_Course_2025/
Session 5 :: Descriptive Statistics
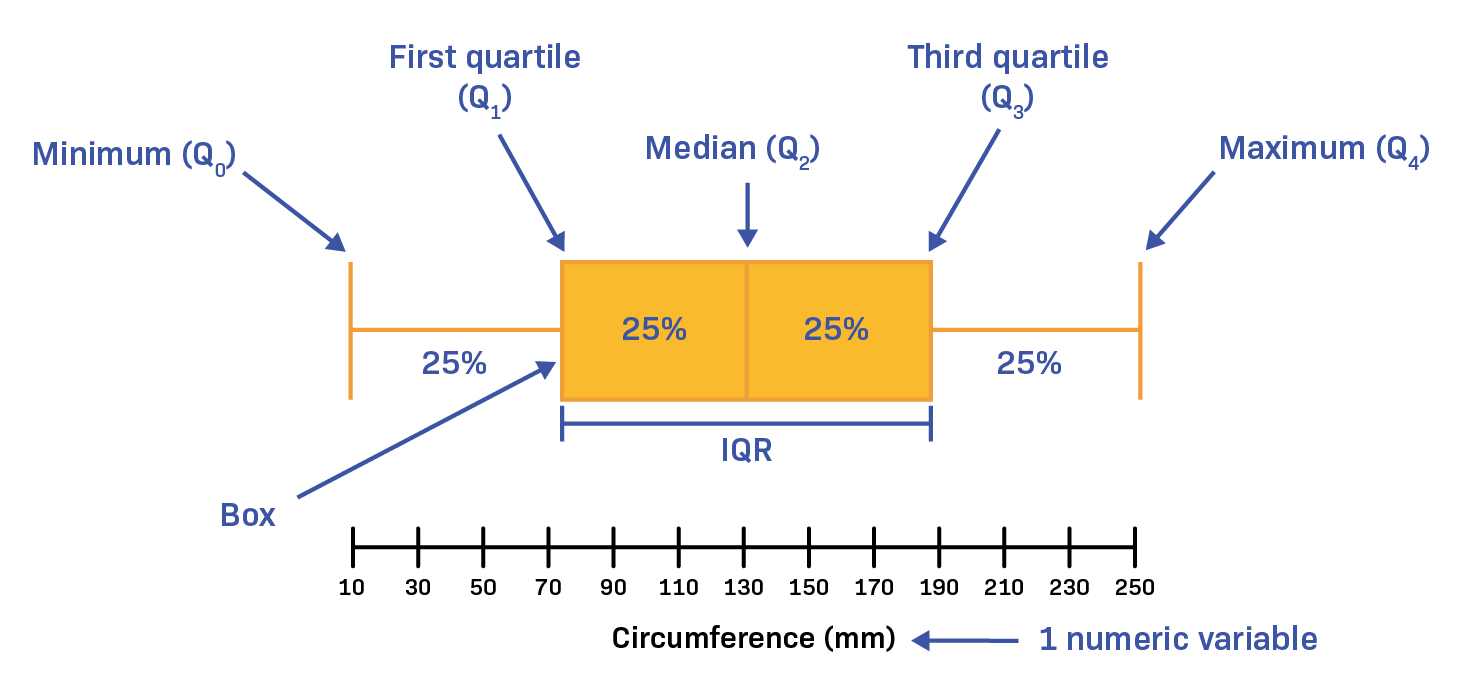
What is Descriptive Statistics ?
descriptive statistics (in the broad sense of the term) is a branch of statistics aiming at summarizing, describing and presenting a series of values or a dataset.
There exists many measures to summarize a dataset. They are broadly divided into three types:
- Central Tendency
- Mean, median, and mode
- Variability
- Range, variance, and standard deviation
- Distribution
- Modality, Skewness, Kurtosis
Measures of Central Tendency
mean, median, mode
3 2.8 3.2 3.4 3.1 2.9 2.7 2.5 3.3 3.5 3.8 2.6 2.3 3.6 2.2 2.4 3.7 3.9 2 4
26 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 6 6 6 5 4 4 3 3 3 2 1 1
4.1 4.2 4.4
1 1 1 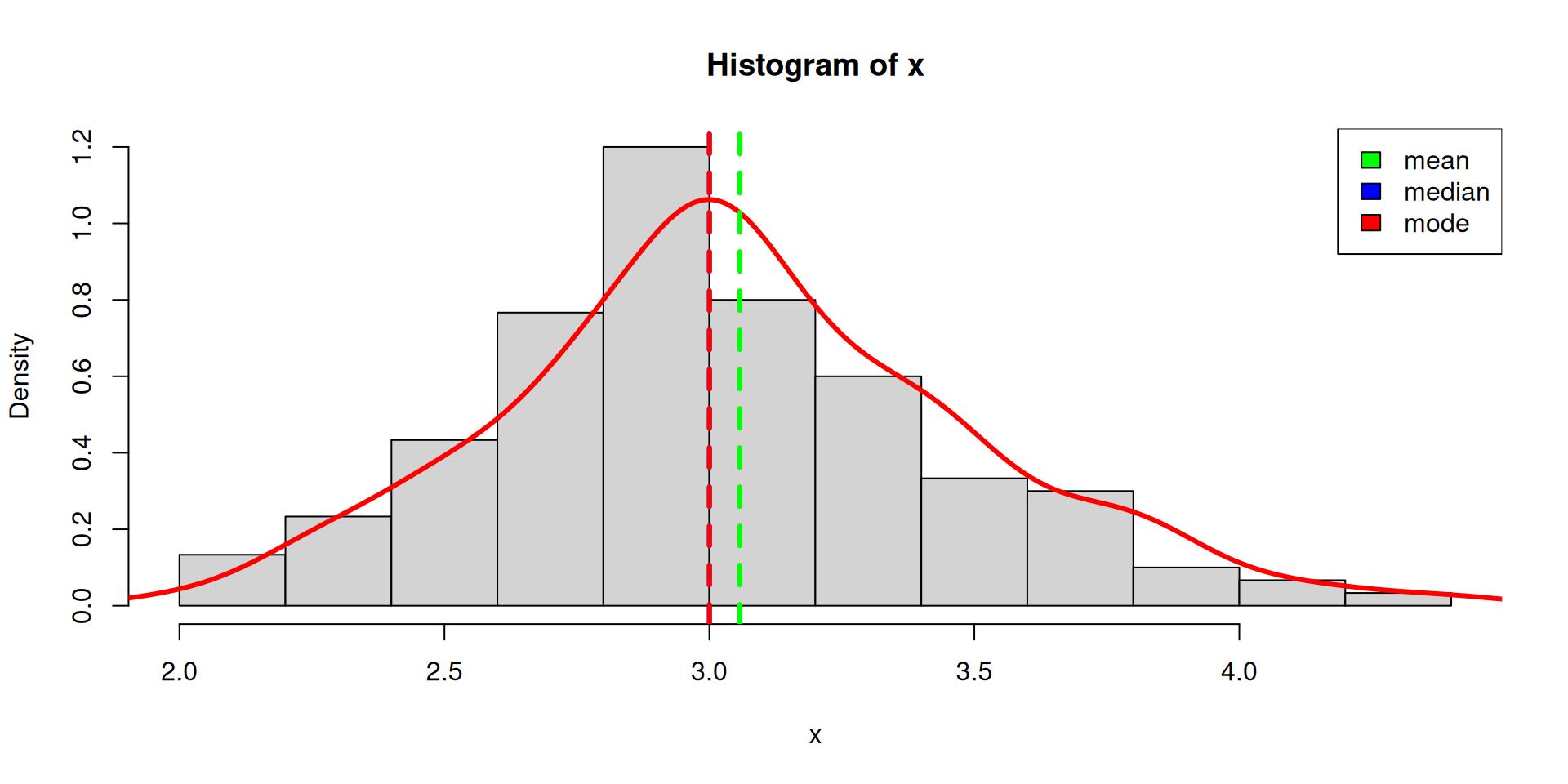
Measures of Variability
Min, max, range
Measures of Distribution
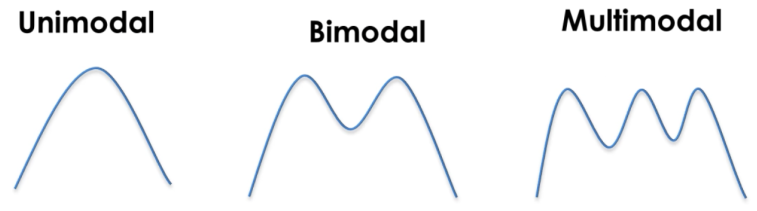
Modes
The modality of a distribution is determined by the number of peaks it contains
Skewness
Skewness is a measurement of the symmetry of a distribution.
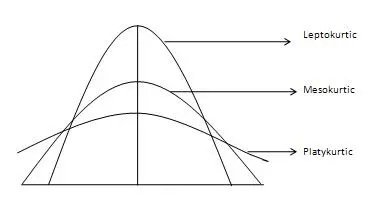
Kurtosis
Kurtosis measures whether your dataset is heavy-tailed or light-tailed compared to a normal distribution.

Descriptive Statistics
Sepal.Length Sepal.Width Petal.Length Petal.Width
Min. :4.300 Min. :2.000 Min. :1.000 Min. :0.100
1st Qu.:5.100 1st Qu.:2.800 1st Qu.:1.600 1st Qu.:0.300
Median :5.800 Median :3.000 Median :4.350 Median :1.300
Mean :5.843 Mean :3.057 Mean :3.758 Mean :1.199
3rd Qu.:6.400 3rd Qu.:3.300 3rd Qu.:5.100 3rd Qu.:1.800
Max. :7.900 Max. :4.400 Max. :6.900 Max. :2.500
Species
setosa :50
versicolor:50
virginica :50
Frequency/Cross/Contingency Tables
Cross-tabulation analysis, also known as contingency table analysis, is most often used to analyze categorical (nominal measurement scale) data.
At their core, cross-tabulations are simply data tables that present the results of the entire group of respondents, as well as results from subgroups of survey respondents. With them, you can examine relationships within the data that might not be readily apparent when only looking at total survey responses
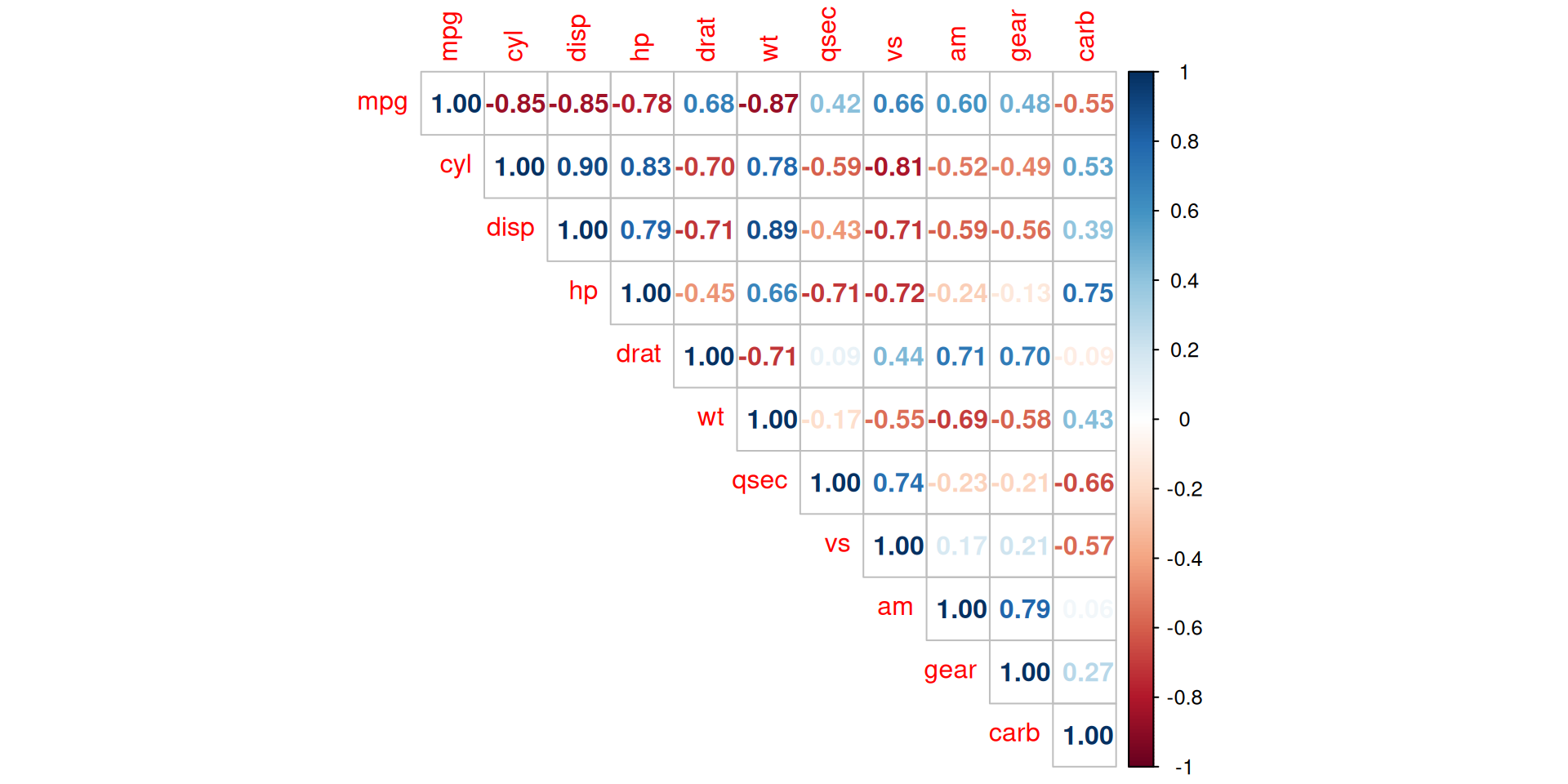
Correlation
Correlation measures the relationship between two variables if they are linked to each other. It denotes if variables evolve in the same direction, in the opposite direction, or are independent.
Correlation is usually computed on two quantitative variables, but it can also be computed on two qualitative ordinal variables.
Pearson correlation is often used for quantitative continuous variables that have a linear relationship
Spearman correlation (which is actually similar to Pearson but based on the ranked values for each variable rather than on the raw data) is often used to evaluate relationships involving at least one qualitative ordinal variable or two quantitative variables if the link is partially linear
Correlation Test
a correlation coefficient different from 0 in the sample does not mean that the correlation is significantly different from 0 in the population. This needs to be tested with a hypothesis test—and known as the correlation test.
The null and alternative hypothesis for the correlation test are as follows:
- H0 : ρ = 0 (meaning that there is no linear relationship between the two variables)
- H1 : ρ ≠ 0 (meaning that there is a linear relationship between the two variables)
Pearson's product-moment correlation
data: iris$Sepal.Length and iris$Sepal.Width
t = -1.4403, df = 148, p-value = 0.1519
alternative hypothesis: true correlation is not equal to 0
95 percent confidence interval:
-0.27269325 0.04351158
sample estimates:
cor
-0.1175698 Session 6 :: More Basic Concepts in R
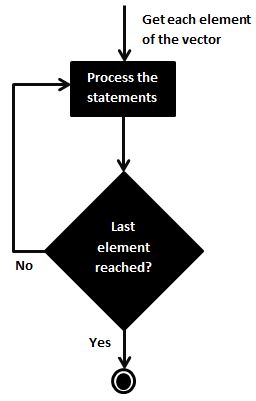
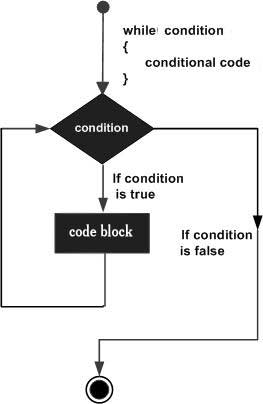
Control Flow
if-elseis used to evaluate whether a statement isTRUEorFALSE- If the statement is
TRUE, the first code block is executed - If the statement is
FALSE, the second code block is executed
R Loops
The apply family
An apply function is essentially a loop, but run faster than loops and often require less code. The apply family of functions is a set of functions in R that allow you to apply a function to the rows or columns of a matrix or data frame. The main functions in the apply family are:
[,1] [,2] [,3]
[1,] 1 11 21
[2,] 2 12 22
[3,] 3 13 23
[4,] 4 14 24
[5,] 5 15 25
[6,] 6 16 26
[7,] 7 17 27
[8,] 8 18 28
[9,] 9 19 29
[10,] 10 20 30lapply is used to apply a function to each element of a list or vector and returns a list. It is useful when you want to apply a function to each element of a list and return the results in a list format.
sapply is a simplified version of lapply. It tries to simplify the result to a vector or matrix if possible.
vapply is similar to sapply, but it requires you to specify the type of output you expect. This can help prevent unexpected results.
tapply is used to apply a function to subsets of a vector, based on a grouping factor. It is useful for performing calculations on subsets of data.
Session 7 :: Practice 1
Session 8 :: Practice 2
Practice 2 ..
- Use
.Rmdor.qmdfile to document your code and results. - Select
irisdataset and create a new dataset with onlySepal.LengthandSepal.Widthcolumns. - Create a new column
Sepal.Areausingcbindin the new dataset by multiplyingSepal.LengthandSepal.Width.- Check if there is any correlation between
Sepal.LengthandSepal.Area. - Create a new column
Sepal.Sizein the new dataset by usingifelsefunction to classifySepal.Areaassmallorbigbased on the median value ofSepal.Area - Create a Contingency Table for
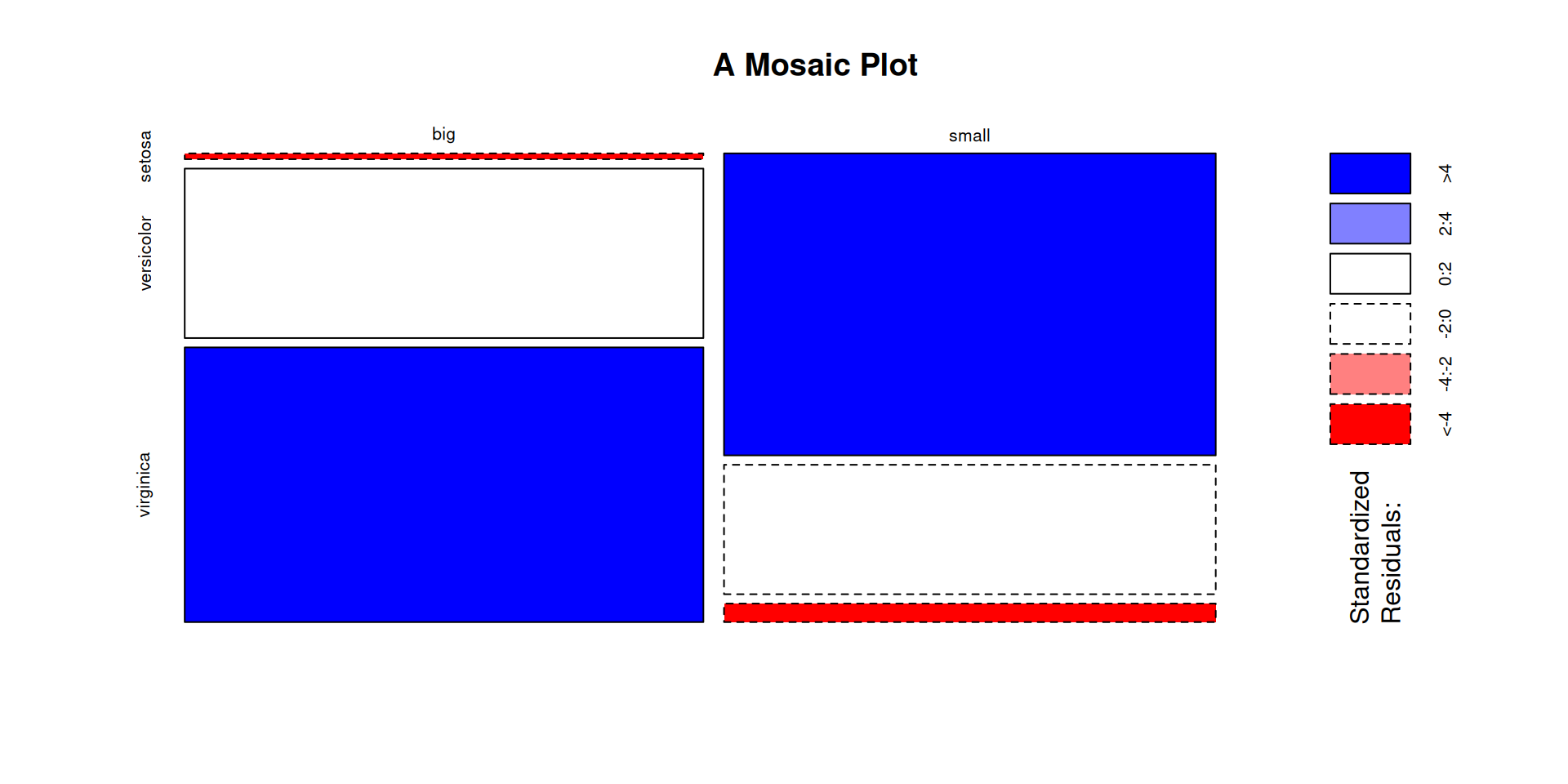
Sepal.Area. - Create a Mosaic Plot for
Sepal.Area. - Create a Histogram for
Sepal.Areaand save it with specific dimension and resolution. - save dataset as
iris_new.csvandiris_new.xlsin the working directory.
- Check if there is any correlation between
Practice 2
- Use
forand/orwhileloop to calculate the mean ofSepal.LengthandSepal.Widthfor each species in the new dataset.- Use
breakstatement to exit the loop when the mean ofSepal.Lengthis greater than 5. - Use
nextstatement to skip the iteration when the mean ofSepal.Lengthis less than 5.
- Use
- Use
applyfamily functions to calculate the mean, median, standard deviation, and standard error ofSepal.LengthandSepal.Widthfor each species in the new dataset.- Use boxplots for
Sepal.LengthandSepal.Widthfor each species in the new dataset.
- Use boxplots for
- Use the
cut()function to create a vector of intervals for each of the four floral traits (see?cut). Then, for each trait, make a contingency table of Species versus the interval factor of that trait, and draw a barplot of this table. In the barplot, there should be one bar per trait interval, with the counts of each species in this interval stacked. Combine the plots for the 4 floral traits into one plot, usinglayout().